Struggling to fall asleep or stay asleep? You’re not alone. Many people are seeking natural, effective ways to improve their sleep quality. Science points to one essential mineral as a game-changer: magnesium. Research shows that magnesium can help regulate sleep patterns and promote relaxation. If you’re wondering how to naturally boost your intake, you’re in the right place. In this guide, we’ll dive into the best foods high in magnesium for sleep and how to use them effectively.
As a health writer specializing in evidence-based wellness content, I’m committed to bringing you well-researched, practical information you can trust.
Why Magnesium is Crucial for a Good Night’s Sleep
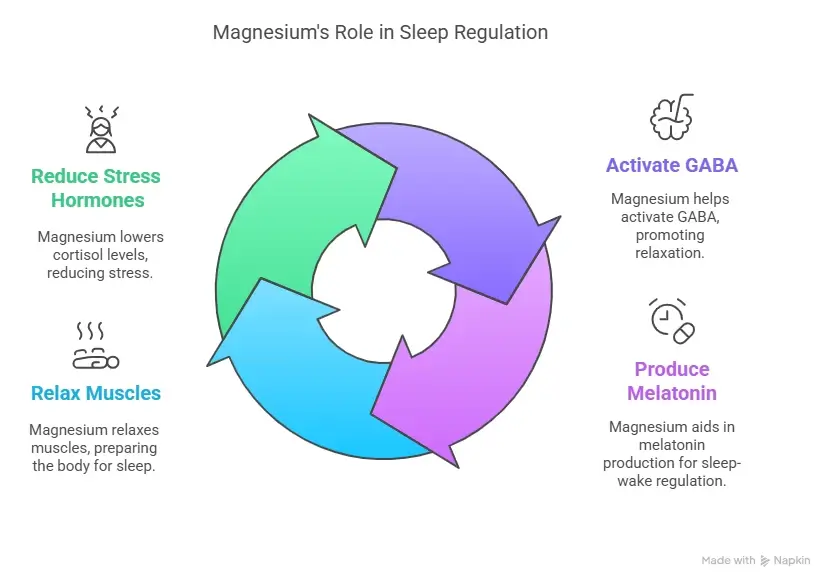
Magnesium plays a critical role in sleep regulation. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- GABA Activation: Magnesium helps activate GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and reduces brain activity, making it easier to drift into sleep.
- Magnesium: helps your body produce melatonin, the hormone that manages your internal sleep-wake clock.
- Muscle Relaxation: Magnesium relaxes the muscles and calms the nervous system, helping you physically prepare for sleep.
- Stress Reduction: It lowers cortisol, the “stress hormone,” which can interfere with your ability to sleep peacefully.
Source: National Institutes of Health (NIH)
Understanding how magnesium helps sleep is the first step toward better rest.
The Top 15 Magnesium-Packed Foods Proven to Aid Sleep
Let’s dig into the best foods high in magnesium for sleep, complete with serving suggestions and tips!
1. Pumpkin Seeds
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 168 mg per 1 ounce (28g)
- Why it Helps Sleep: Exceptionally rich in magnesium and tryptophan.
- Tips: Snack on roasted pumpkin seeds in the evening or sprinkle them on salads.
2. Spinach
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 157 mg per cooked cup
- Why it Helps Sleep: Loaded with magnesium and folate, supporting relaxation.
- Tips: Steam lightly and toss with olive oil for a quick side dish.
3. Almonds
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 77 mg per ounce
- Why it Helps Sleep: Also provides healthy fats and melatonin.
- Tips: Enjoy a handful as a pre-bedtime snack.
4. Black Beans
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 120 mg per cooked cup
- Why it Helps Sleep: High in fiber and protein for blood sugar balance.
- Tips: Add to soups or burrito bowls for dinner.
5. Dark Chocolate (70% cacao or higher)
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 64 mg per ounce
- Why it Helps Sleep: Contains antioxidants that reduce stress.
- Tips: Enjoy a small piece after dinner.
6. Avocado
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 58 mg per medium fruit
- Why it Helps Sleep: Also rich in potassium and healthy fats.
- Tips: Mash on whole-grain toast or add to smoothies.
7. Tofu
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 53 mg per 3.5 ounces (100g)
- Why it Helps Sleep: A plant-based protein powerhouse.
- Tips: Stir-fry with vegetables for a quick dinner.
8. Banana
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 32 mg per medium banana
- Why it Helps Sleep: High in magnesium and potassium.
- Tips: Slice into oatmeal for an evening snack.
9. Cashews
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 82 mg per ounce
- Why it Helps Sleep: Good source of zinc and healthy fats.
- Tips: Mix into trail mix or yogurt parfaits.
10. Swiss Chard
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 150 mg per cooked cup
- Why it Helps Sleep: Packed with magnesium and fiber.
- Tips: Sauté with garlic and olive oil.
11. Mackerel
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 82 mg per 3 ounces
- Why it Helps Sleep: Rich in magnesium and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Tips: Grill with lemon and herbs.
12. Edamame
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 50 mg per ½ cup cooked
- Why it Helps Sleep: High in protein and magnesium.
- Tips: Snack on steamed edamame sprinkled with sea salt.
13. Brown Rice
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 86 mg per cooked cup
- Why it Helps Sleep: Complex carbs help relax the brain.
- Tips: Serve with grilled veggies.
14. Quinoa
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 118 mg per cooked cup
- Why it Helps Sleep: Complete protein and magnesium-rich.
- Tips: Make quinoa salad with leafy greens.
15. Yogurt
- Magnesium Content: Approx. 45 mg per cup
- Why it Helps Sleep: Contains probiotics and magnesium.
- Tips: Enjoy with a sprinkle of pumpkin seeds.
Quick Reference Table
| Food | Serving Size | Magnesium Content |
| Pumpkin Seeds | 1 oz | 168 mg |
| Spinach (cooked) | 1 cup | 157 mg |
| Almonds | 1 oz | 77 mg |
| Black Beans | 1 cup | 120 mg |
| Dark Chocolate | 1 oz | 64 mg |
| Avocado | 1 fruit | 58 mg |
| Tofu | 100g | 53 mg |
| Banana | 1 medium | 32 mg |
| Cashews | 1 oz | 82 mg |
| Swiss Chard | 1 cup | 150 mg |
| Mackerel | 3 oz | 82 mg |
| Edamame | ½ cup | 50 mg |
| Brown Rice | 1 cup | 86 mg |
| Quinoa | 1 cup | 118 mg |
| Yogurt | 1 cup | 45 mg |
How Much Magnesium Do You Actually Need for Sleep?
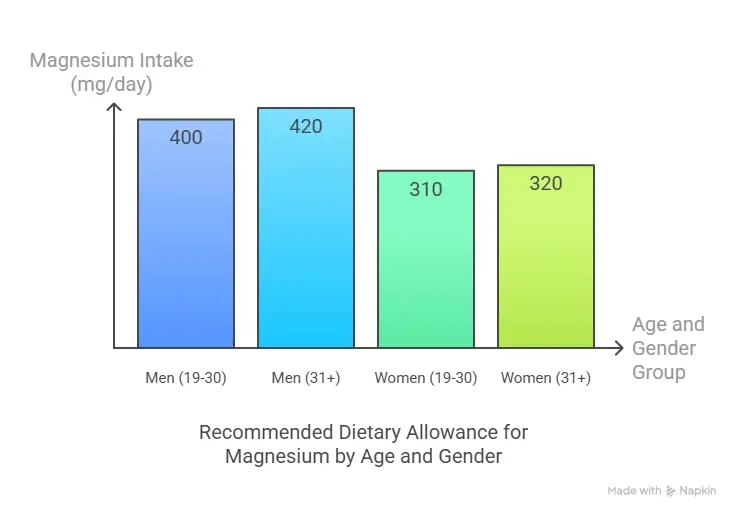
According to the NIH, the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for magnesium is:
- Men (ages 19-30): 400 mg/day
- Men (ages 31+): 420 mg/day
- Women (ages 19-30): 310 mg/day
- Women (ages 31+): 320 mg/day
Source: NIH Magnesium Fact Sheet
While optimal magnesium levels for sleep aren’t officially established, meeting or slightly exceeding these RDAs through food can significantly support better rest.
Delicious & Easy Ways to Boost Your Magnesium Intake Before Bed
Here are simple, tasty ways to add magnesium to your evening routine:
- Snack Idea: A banana with a handful of almonds.
- Dinner Idea: Grilled mackerel with quinoa and steamed spinach.
- Evening Smoothie: Banana, spinach, avocado, and almond milk.
- Magnesium-Rich Meal Plan:
- Dinner: Brown rice bowl with tofu and Swiss chard.
- Evening Snack: Pumpkin seeds and a square of dark chocolate.
Food Prep Tips
- Lightly steam greens to preserve magnesium.
- Opt for whole grains over refined grains.
- Choose raw or dry-roasted nuts without added oils.

Foods vs. Supplements: What You Need to Know
Supplements are an option, but food should be your first choice.
Pros of Food Sources:
- Higher bioavailability
- Provide synergistic nutrients
- Lower risk of overdose
Cons of Supplements:
- Potential for gastrointestinal upset
- Risk of excessive intake
Important: Always consult a healthcare provider before starting magnesium supplements, especially if you have health conditions or take medications.

Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to consume too much magnesium through food?
- It’s rare because the kidneys efficiently eliminate excess magnesium from food. Overconsumption issues usually stem from supplements.
How quickly can magnesium-rich foods improve sleep?
- Some people notice improvements within a week, but consistency over time yields the best results.
What are signs of magnesium deficiency affecting sleep?
- Symptoms may include trouble falling asleep, frequent waking, muscle cramps, irritability, and fatigue.
Conclusion
Incorporating foods high in magnesium for sleep into your diet is a delicious, accessible way to boost your rest naturally. Remember these powerhouse foods: pumpkin seeds, spinach, almonds, and dark chocolate.
Ready to start? Try adding just one or two magnesium-rich foods into your evening meals and see how you feel. Don’t forget to check out our related articles like “[Complete Guide to Sleep Hygiene]” and “[Other Nutrients That Support Sleep]” for even more tips!
Sweet dreams!
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
